Prototyping with
3D printing Service
What We Offer
INAC US’s Prototyping 3D Printing service rapidly turns complex designs into tangible prototypes using advanced 3D printing technology. Our service is ideal for intricate structures, undercut shapes, and designs needing quick verification.
We utilize highly transparent, moisture-resistant materials like TSR-829, ensuring precision and quality in every product. From initial 3D data provision to final finishing and transparentizing, our process is efficient and detail-oriented, even accommodating decorative elements like coating and plating.
Choose INAC US for fast, accurate, and versatile 3D printed prototyping solutions.
Materials We Handle
- TSR829 (highly transparent stereolithography material)
- Durable/Elastic 50A/Standard (Clear/White/Black)/Flexible Resin 80A
- PA2200 (Nylon)
Equipments for 3D Printing
| Machine | Manufacturer | Product / model name | Specifications X / Y / Z (inches) | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stereolithography equipment | CMET Inc. | ATOMm-4000 | D15.75/W15.75/H11.81 | 2 |
| Stereolithography equipment | CMET Inc. | ATOMm-8000 | D31.5/W23.62/H15.75 | 1 |
| Stereolithography equipment | Formlabs Inc. | Formlabs Form 3 | – | 1 |
3D Printing Methods
Stereolithography (SLA)
Stereolithography(SLA) is a modeling method for 3D printers in which a tank of liquid photocurable resin is irradiated with ultraviolet laser light with the purpose of being able to harden and stack layers one by one.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
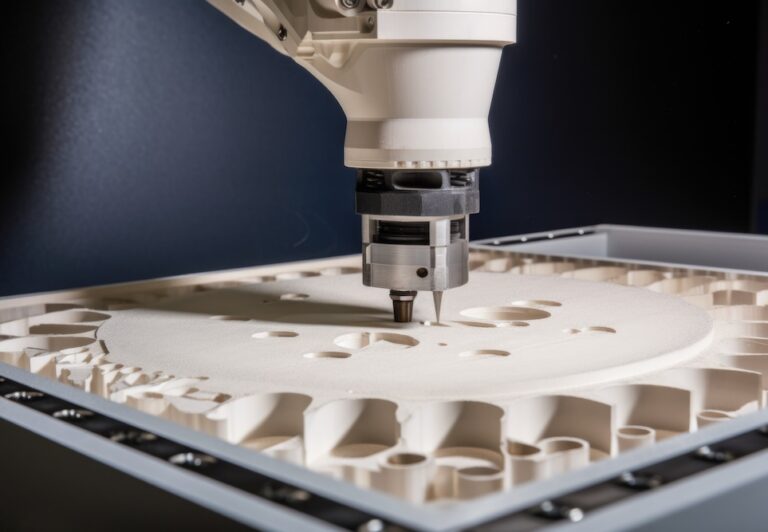

Selective Laser Sintering(SLS) is one of the more prominent modeling methods for 3D printers. It is a method in which a powdered material (resin or metal) is irradiated with a laser beam and sintered layer by layer, to form a shape.
3D Printing Tolerances
Stereolithography (SLA)
| Specifications | Value, inches |
|---|---|
| Max Part Size | D31.50/W23.62/H15.75 |
| Min Feature Size | φ0.394 |
| Tolerances | ±0.004 |
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
| Specifications | Value, inches |
|---|---|
| Max Part Size | 13.39×13.39×24.41 |
| Min Feature Size | φ0.394 |
| Tolerances | ±0.012 |
Past Works
Internal visualization
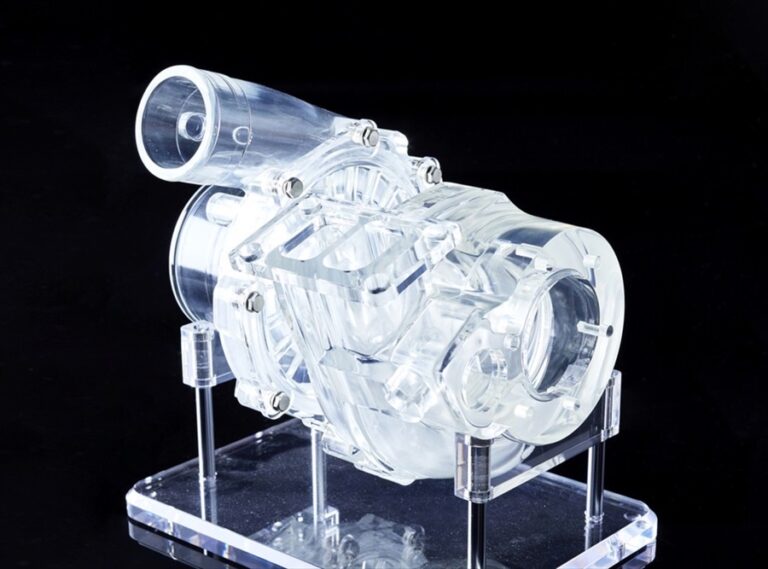
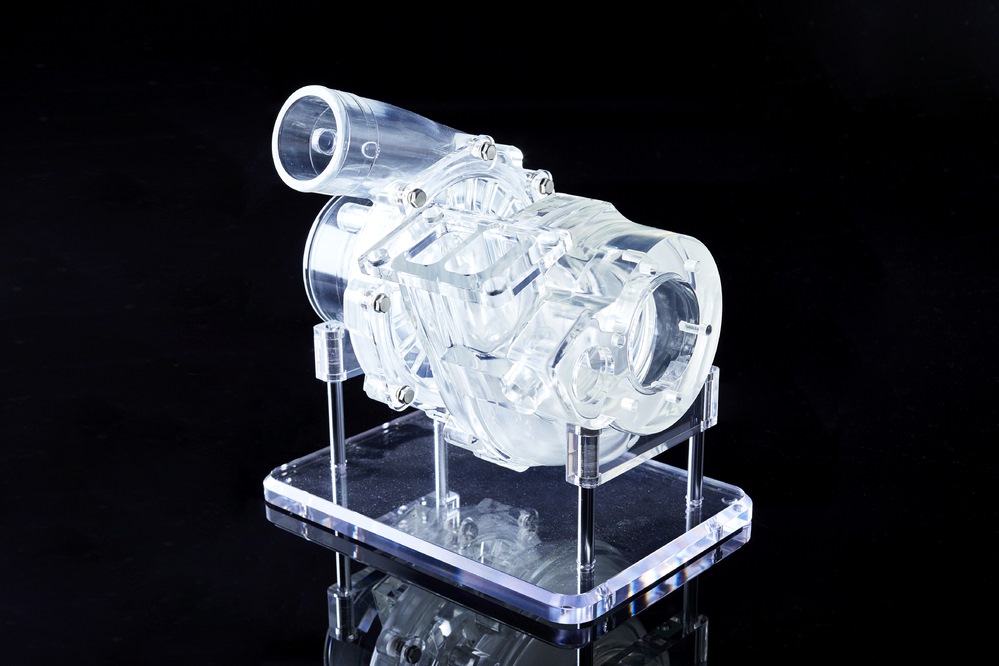
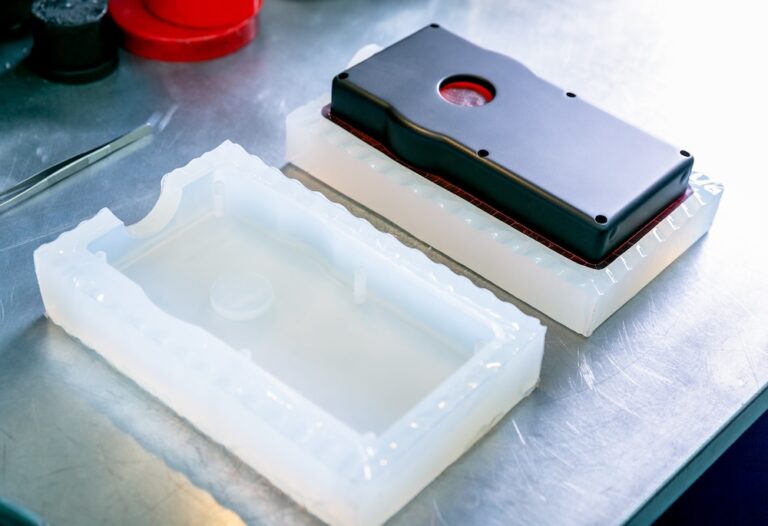
High transparency stereolithography prototype
Method: 3D printing (STL: stereolithography)
Our company, INAC, which specializes in machined high-transparency products, is committed to provide high-transparency stereolithography model products.
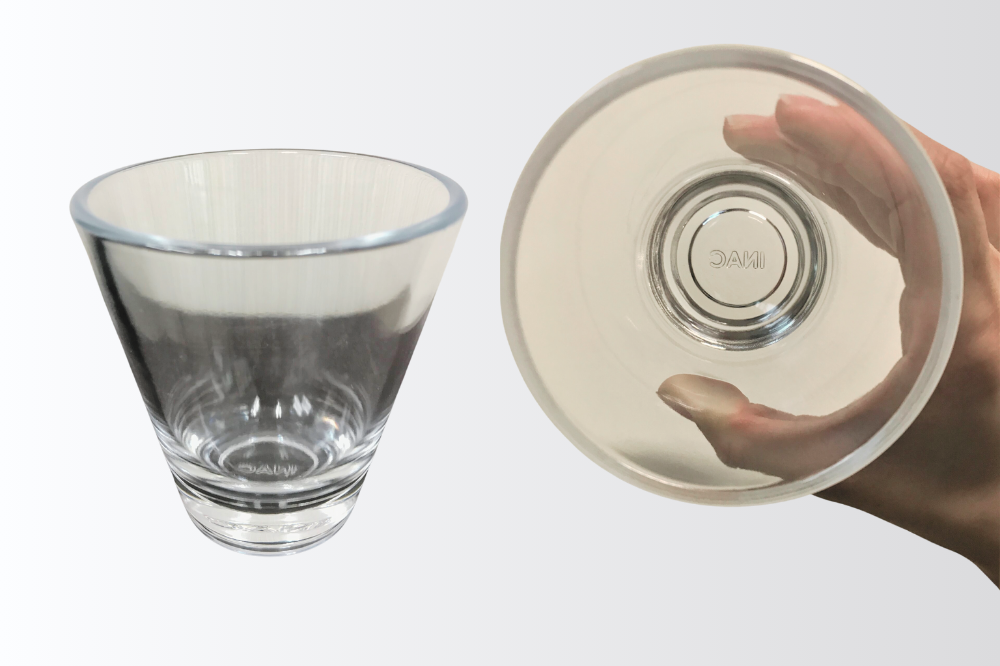
3D printed glass cup
HIGHLY TRANSPARENT STEREOLITHOGRAPHY
- Special technique enables highly transparent 3d printing with minimum bubbles.
- Material: TSR 829 (Moisture-resistant highly transparent materials)
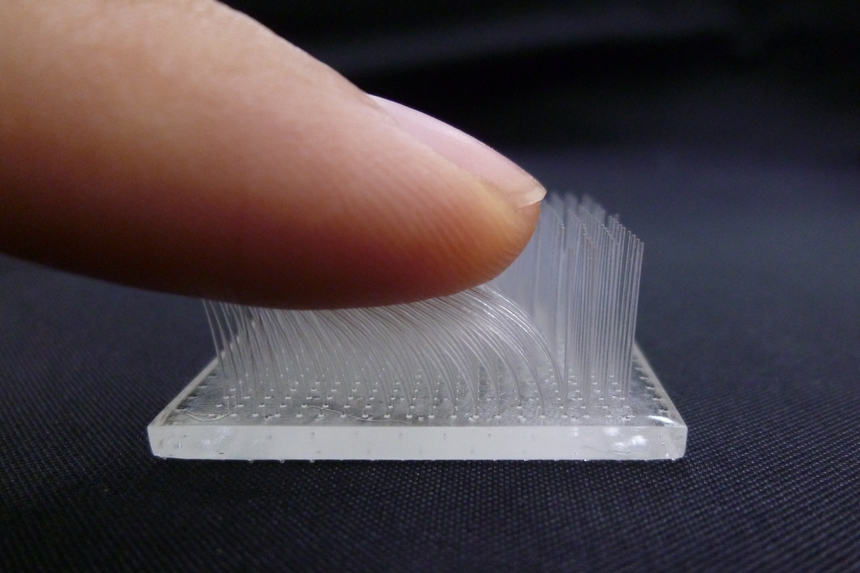
3D printed fine brush
Diameter is approximately φ0.24mm. Flexible enough and hard to break. Best printing condition is applied based on our adequate experience.
Material: TSR 829 (Moisture-resistant highly transparent materials)
Size: 30×60×15mm (diameter: φ0.24mm)
vs. Other Processing Methods
vs. Injection Molding
Advantages of 3D printing:
- Capable of creating complex 3D geometries
- Offers high precision and accuracy
- Works with a wide range of materials
- Allows for easy design changes and iterations
Disadvantages of 3D printing:
- Can be less cost-effective and slower for mass production
- Tool accessibility may limit the complexity of parts
vs. Vacuum Casting
Advantages of 3D printing:
- High precision and accuracy
- Capable of creating complex 3D geometries
- Works with a wide range of materials
Disadvantages of 3D printing:
- Can be less cost-effective and slower for producing large quantities of parts
- Tool accessibility may limit the complexity of parts
FAQs
Maximum processing sizes are as follows:
- Stereolithography (SLA): D31.50/W23.62/H15.75
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS):D13.39/W13.39/H24.41
We can handle following 3 types of materials for 3D processing:
- TSR829 (highly transparent stereolithography material)
- Durable/Elastic 50A/Standard (Clear/White/Black)/Flexible Resin 80A
- PA2200 (Nylon)
The following factors affect cost: material, form, dimensional accuracy, finish level, delivery date, quantity.
We can accept solid 3D CAD models in IGES (.igs), STEP (.stp), PARASOLID(.x_t) or STL(.stl).
Get In Touch!
If you have something you want to make, please contact us. Even a rough idea is OK.
We will give shape to your idea and deliver it to you. Please feel free to contact us.